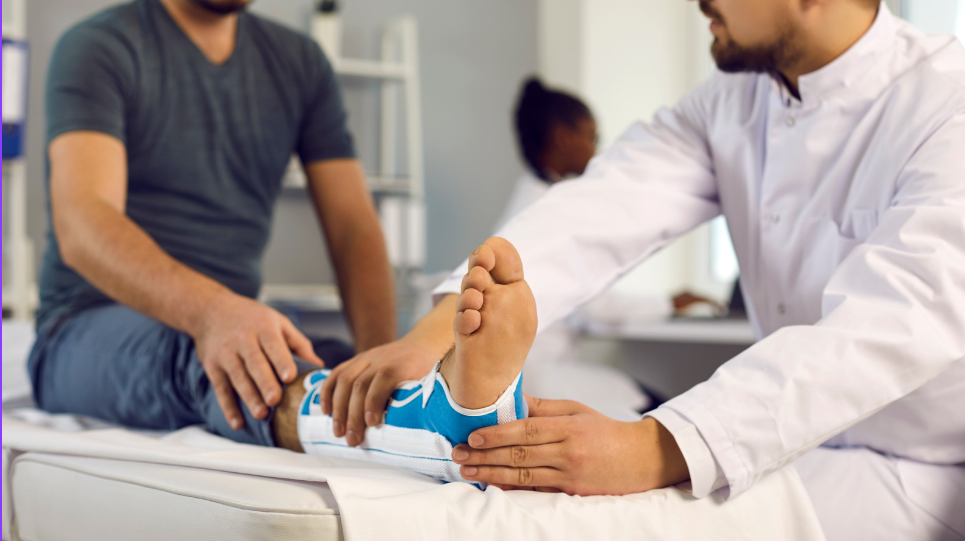
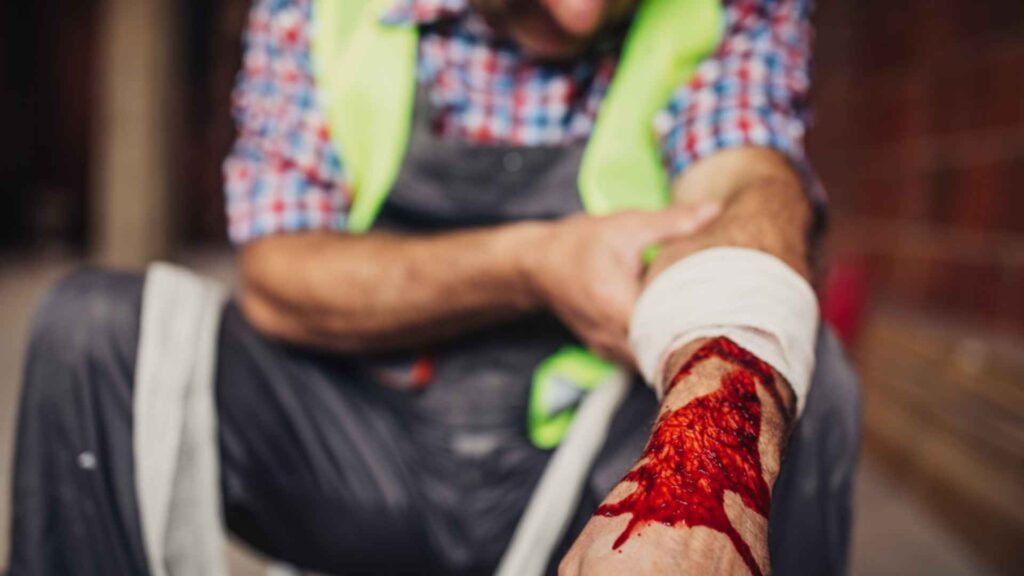
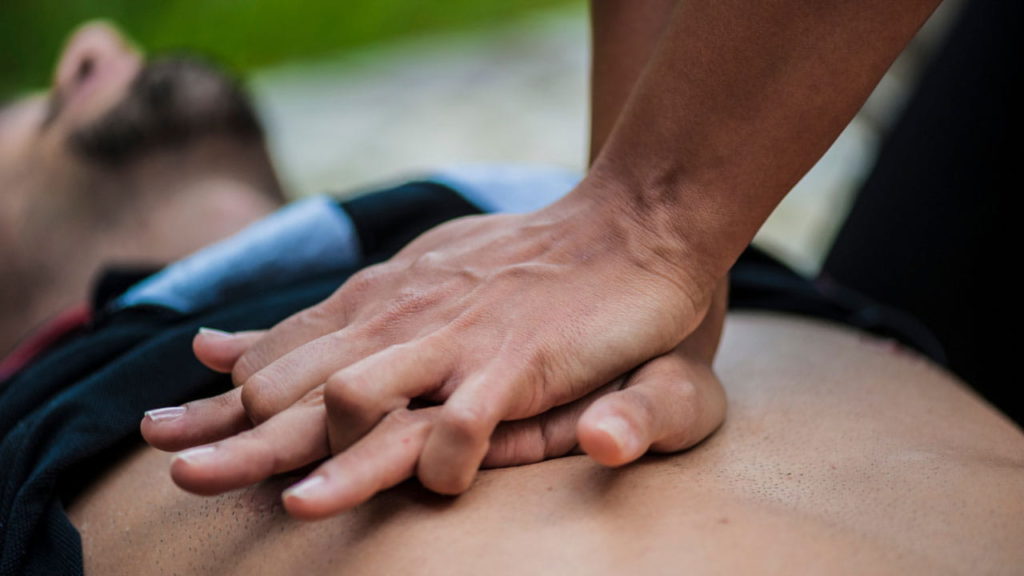
Broken bones, also known as fractures, are a common injury that can occur in various situations, from sports accidents to falls. If the pain lasts longer than usual, it’s difficult to move the injured area, or there’s swelling, it could be a broken bone. Knowing how to provide immediate first aid is crucial in minimizing pain, preventing further damage, and ensuring the best possible outcome for the injured person.
Understanding Fractures
A fracture is a break or crack in a bone. They can range from simple hairline fractures to complex breaks that shatter the bone into multiple pieces. Open fractures involve a break in the skin, posing a higher risk of infection. Broken bones might be unstable, causing internal bleeding, as well as failure to handle them carefully might result in serious injuries or shock. Bone fractures can be of several types – Closed (simple) fracture, Closed (compound) fracture, Greenstick fracture, Hairline fracture, Complicated fracture, Comminuted fracture, Avulsion fracture and Compression fracture.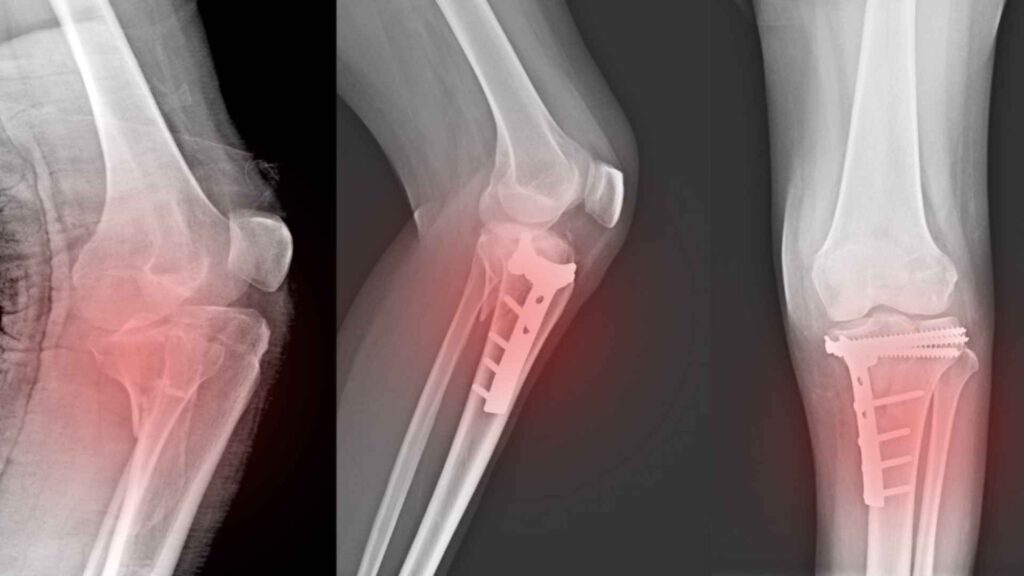
Recognizing the Signs
-
Pain
-
Swelling
-
Deformity
-
Loss of Function
-
Grating Sensation
-
Bruising
Immediate First Aid Steps: ABCs
In any emergency situation, quickly assess the scene to ensure safety for yourself and others (Check). If the person is unresponsive or showing signs of a life-threatening condition, call 9-1-1 immediately (Call). While waiting for help, check the person’s ABCs (Care):
- Airway: Is it open and clear?
- Breathing: Are they breathing normally?
- Circulation: Do they have a pulse?
If needed, start CPR and use an AED if available (Defibrillation). Remember, prioritize life-threatening conditions like unresponsiveness, abnormal breathing, and severe bleeding. If the person is responsive, assess and provide care for the broken bone, following the guidelines in this blog.
Coast2Coast provides First Aid and CPR Training that helps people save lives. Get Registered today and be a hero!
Be Prepared for Fractures!
Join our Standard First Aid Training focused on broken bones and learn essential techniques to assess and manage injuries effectively. Equip yourself with the knowledge to provide immediate care in emergencies.
Stabilizing and Immobilizing a Fracture
1. Control Bleeding
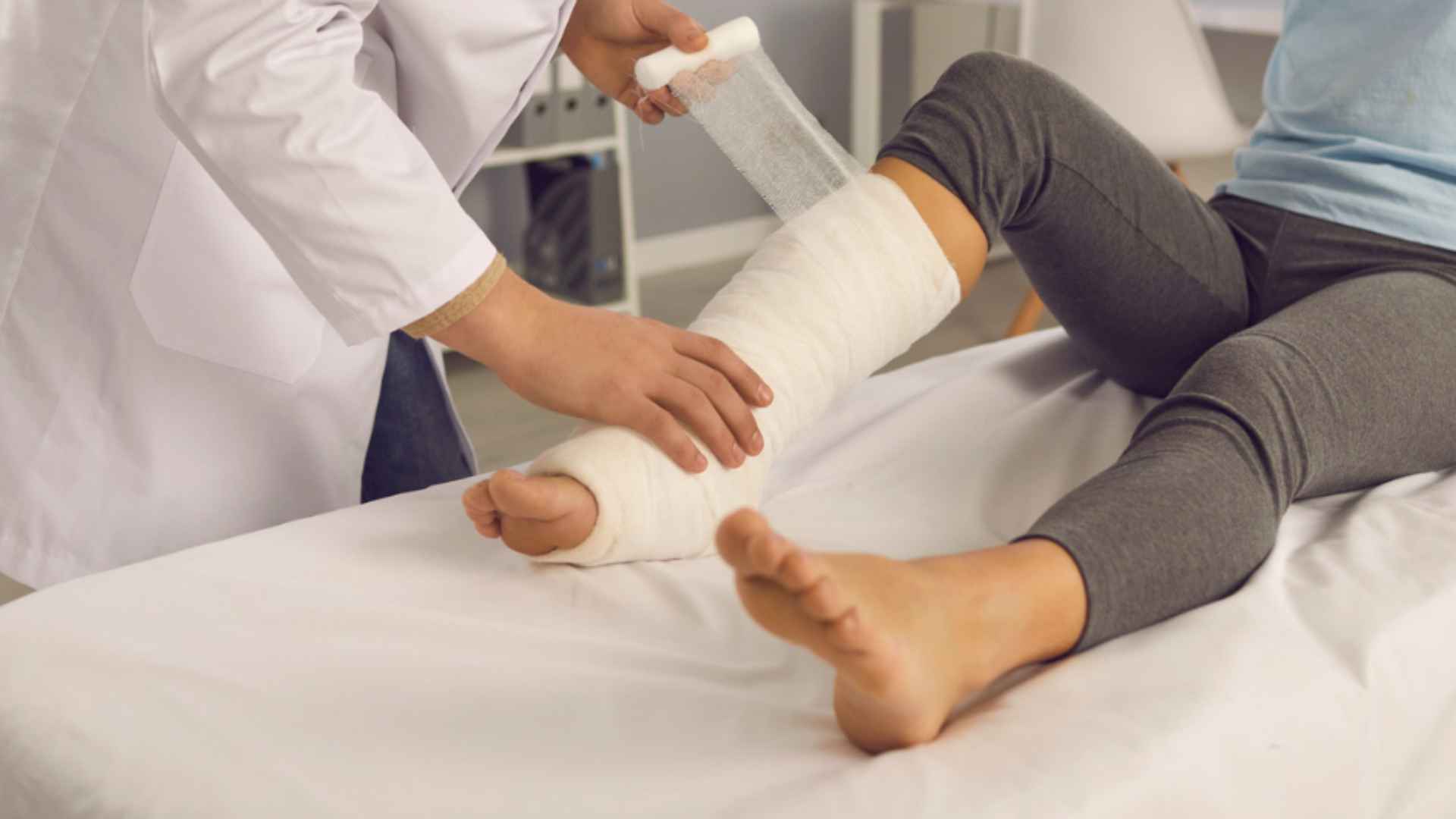
2. Immobilize the Injured Area
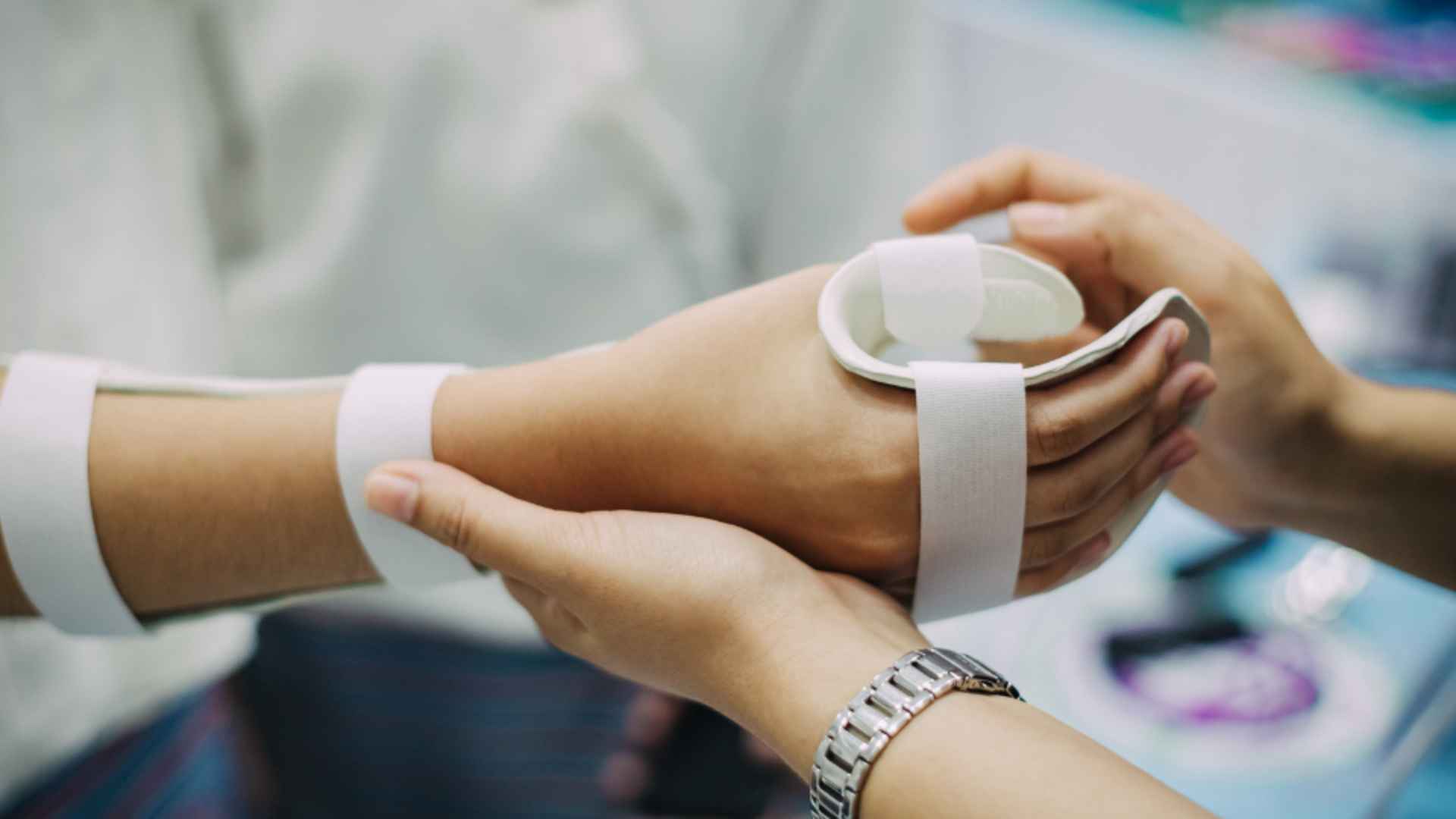 Keep the injured area as still as possible. This can be achieved by:
Keep the injured area as still as possible. This can be achieved by:
- Using Splints: Apply padded splints to support the limb above and below the fracture site.
- Slings: If the collarbone is fractured, use a sling to support the arm on the injured side.
- Bandages: Use broad bandages to gently immobilize the joints above and below the fracture. Ensure that the bandages are properly wrapped- not too loose and not too tight.
3. Elevate
 If possible, raise the injured limb above the heart to help reduce swelling. If it is too painful, you can skip this step.
If possible, raise the injured limb above the heart to help reduce swelling. If it is too painful, you can skip this step.
4. Apply Ice
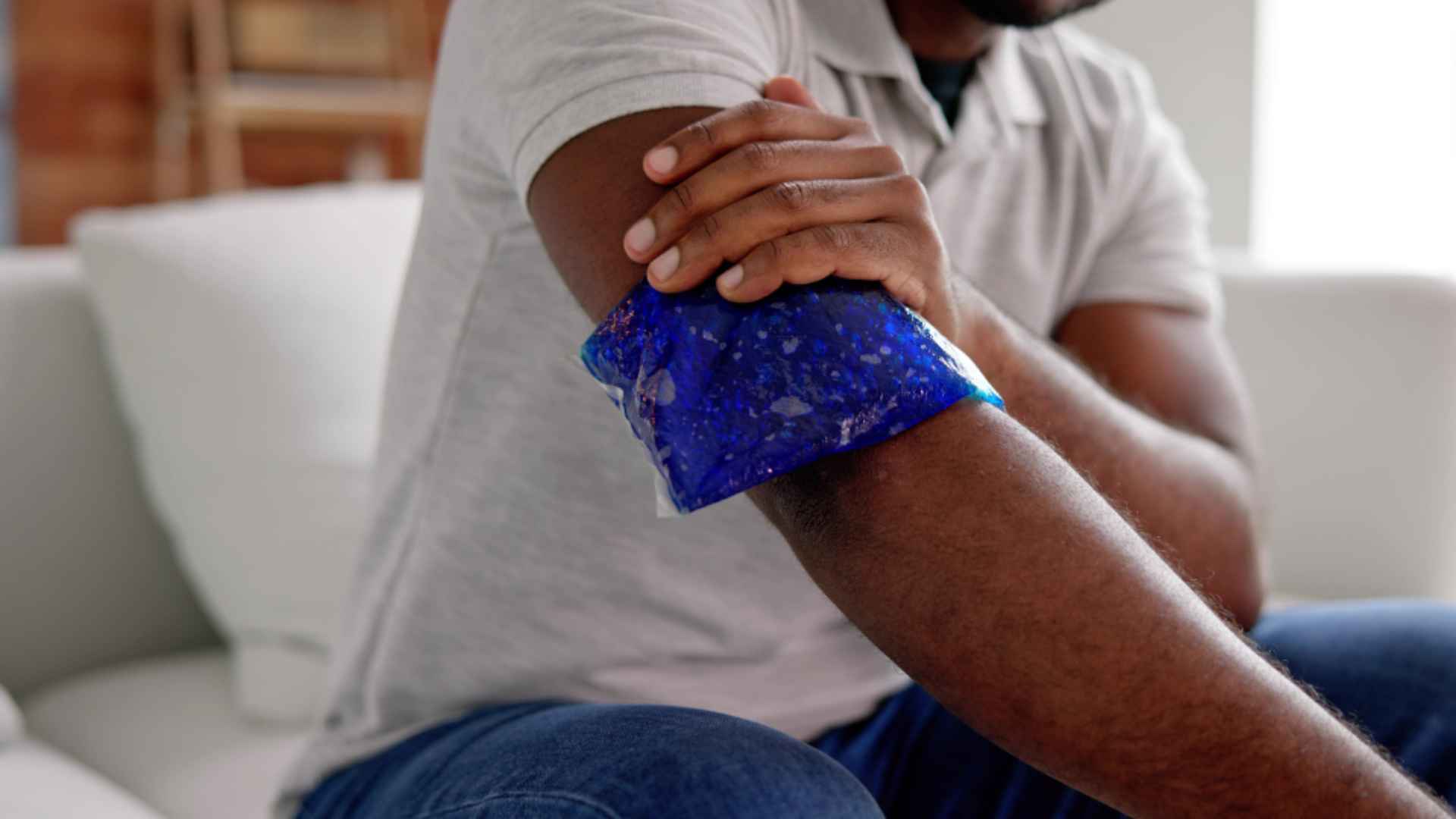 Use ice packs wrapped in a cloth to minimize swelling and pain. First Aid suggests putting a folded gauze pad or cloth between the ice pack and the skin to prevent infections or skin damage. Cold compresses are not advised to be applied directly to an open fracture.
Use ice packs wrapped in a cloth to minimize swelling and pain. First Aid suggests putting a folded gauze pad or cloth between the ice pack and the skin to prevent infections or skin damage. Cold compresses are not advised to be applied directly to an open fracture.
5. Monitor for Shock
Watch for signs of shock, such as pale skin, rapid breathing, and a weak pulse. If shock is suspected, lie the person down, elevate their legs, and keep them warm. If the victim is not breathing or has become unconscious due to pain or any other reason, begin CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) immediately.6. Seek Medical Attention
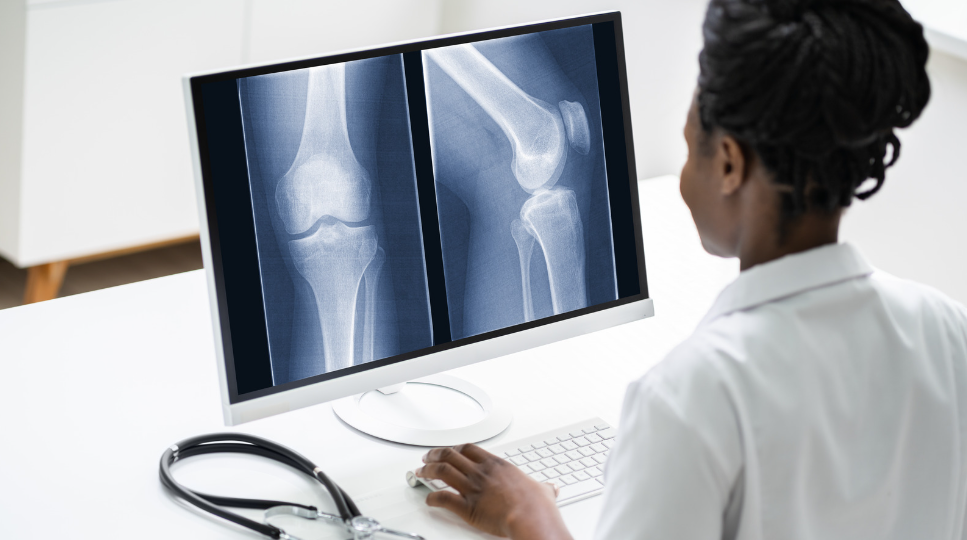 Even if the injury seems minor, it’s crucial to have a doctor assess and treat the fracture to ensure proper healing. A broken bone might lead to several complications. Hence, seeking proper medical assistance is essential to avoid any life-threatening emergency.
Even if the injury seems minor, it’s crucial to have a doctor assess and treat the fracture to ensure proper healing. A broken bone might lead to several complications. Hence, seeking proper medical assistance is essential to avoid any life-threatening emergency. Important Considerations:
-
Do Not Attempt to Realign the Bone
-
Moving an Injured Person
-
Regularly Check Circulation
-
Pain Management
-
Psychological First Aid
-
Being Extra Gentle with Children
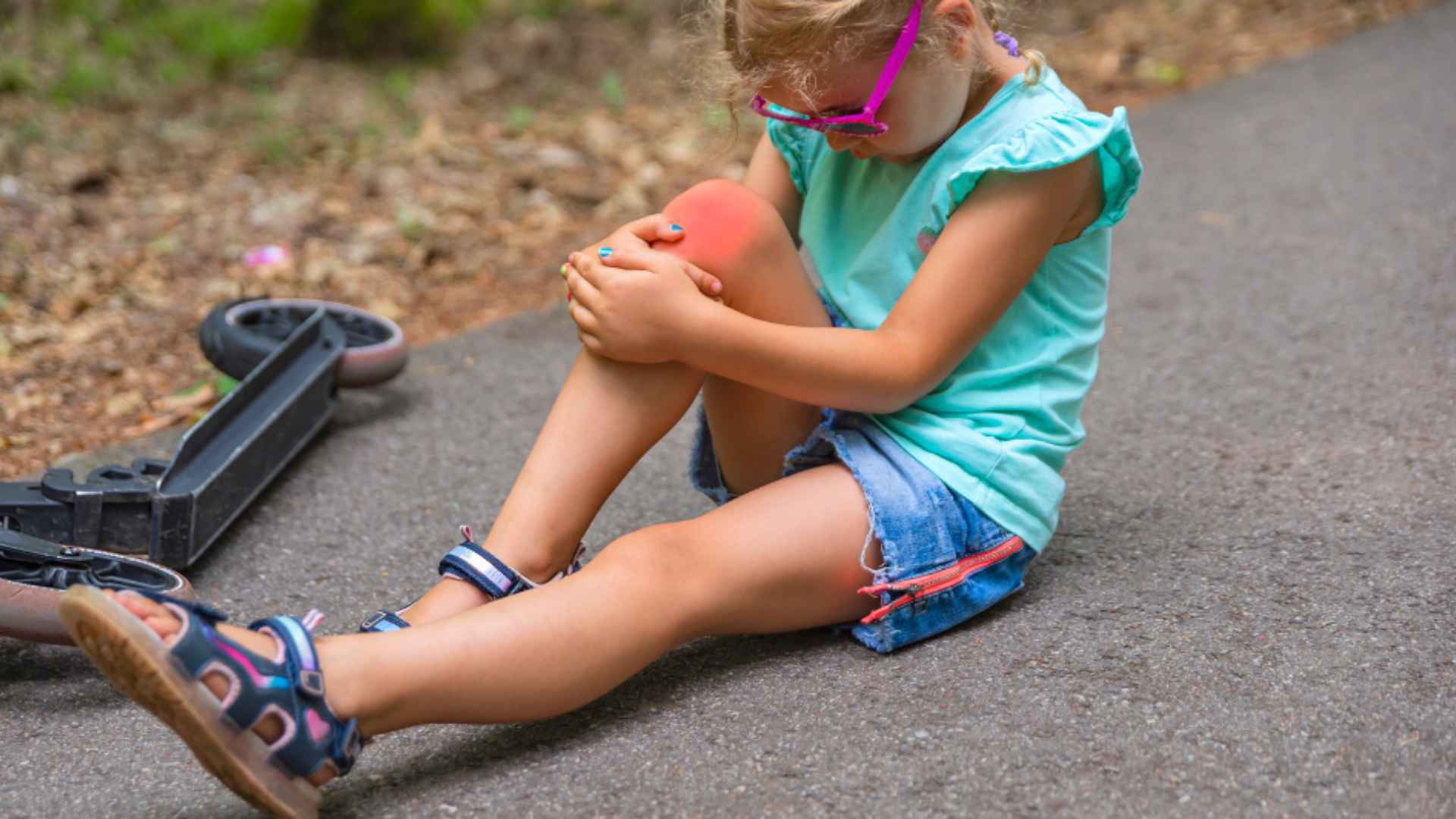 When dealing with fractures in children, it’s advised to be extra gentle and provide extra comfort because children might get scared or stressed out, which could worsen the problem.
When dealing with fractures in children, it’s advised to be extra gentle and provide extra comfort because children might get scared or stressed out, which could worsen the problem.