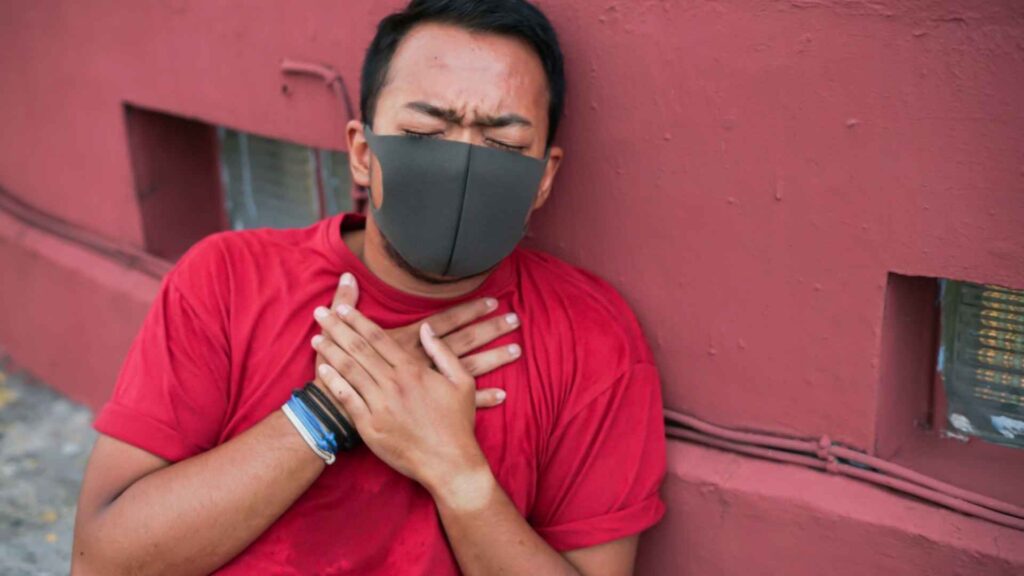
Inhaling unexpected fumes or chemicals can be a frightening experience. Whether at home, work, or in public, a chemical inhalation incident can cause respiratory distress, coughing, and irritation. Knowing how to react quickly and safely in these situations is crucial. This blog post will equip you with the essential knowledge of first aid for chemical inhalation incidents, ensuring you can respond effectively until medical help arrives.
Spot the Signs: Is That a Chemical Attack? Importance of Recognizing Chemical Inhalation
 The first step in responding to a chemical inhalation incident is recognizing it. Symptoms can vary depending on the chemical inhaled, its concentration, and the duration of exposure. Here are some common signs to watch for:
The first step in responding to a chemical inhalation incident is recognizing it. Symptoms can vary depending on the chemical inhaled, its concentration, and the duration of exposure. Here are some common signs to watch for:- Respiratory problems: Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing
- Burning sensation: Burning in the nose, throat, or chest
- Eye irritation: Tearing, redness, blurred vision
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache and dizziness
- Disorientation and confusion
Escape the Danger Zone: Steps to Take in a Chemical Inhalation Incident
When faced with a suspected chemical inhalation incident, immediate action is crucial. Here’s what to do:- Prioritize Safety and Call for Help: If you suspect a chemical inhalation incident, prioritize your safety and the safety of others. Evacuate the area if possible and call emergency services (9-1-1 in Canada) immediately if someone struggles to breathe or their responsiveness is altered. Provide as much information as possible about the situation, including the suspected chemical, the number of people affected, and any symptoms observed.
- Assess the Victim: If the situation is safe to do so, assess the victim’s condition. Look for signs of respiratory distress, such as difficulty breathing, coughing, or wheezing. Check their level of responsiveness. Call poison control if the victim’s ABCs are unaffected and they are alert.
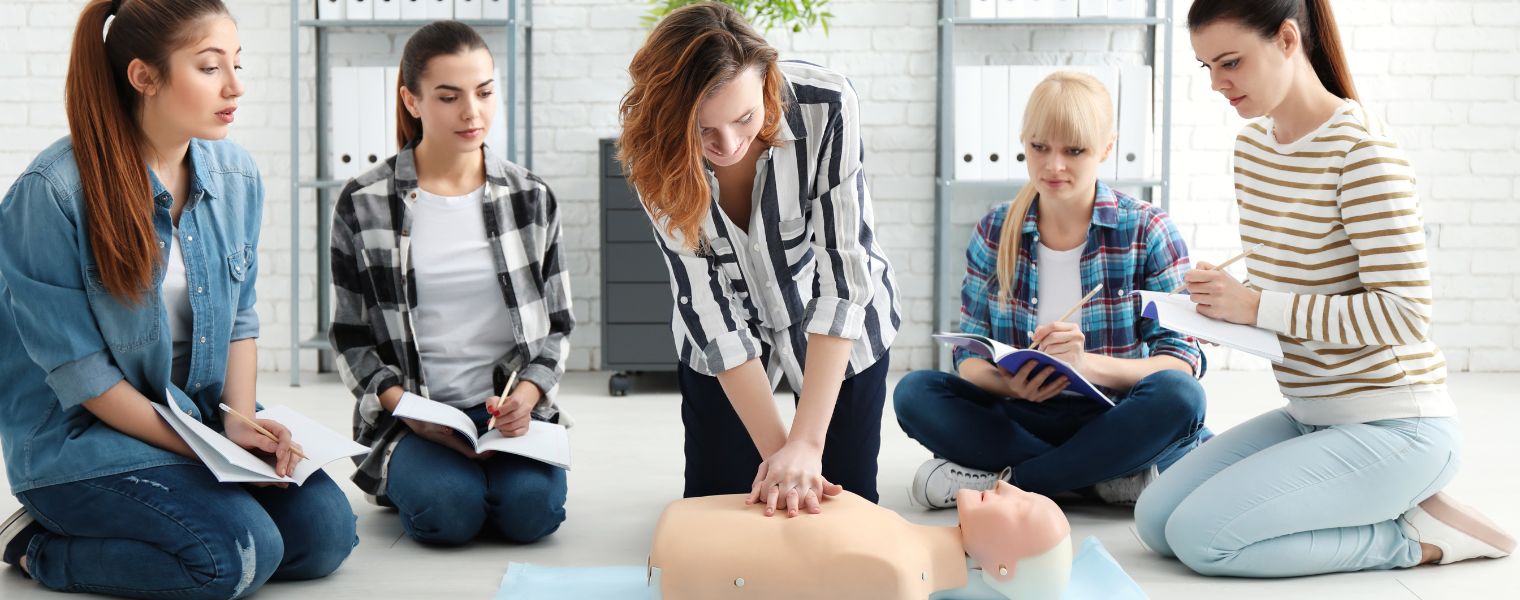
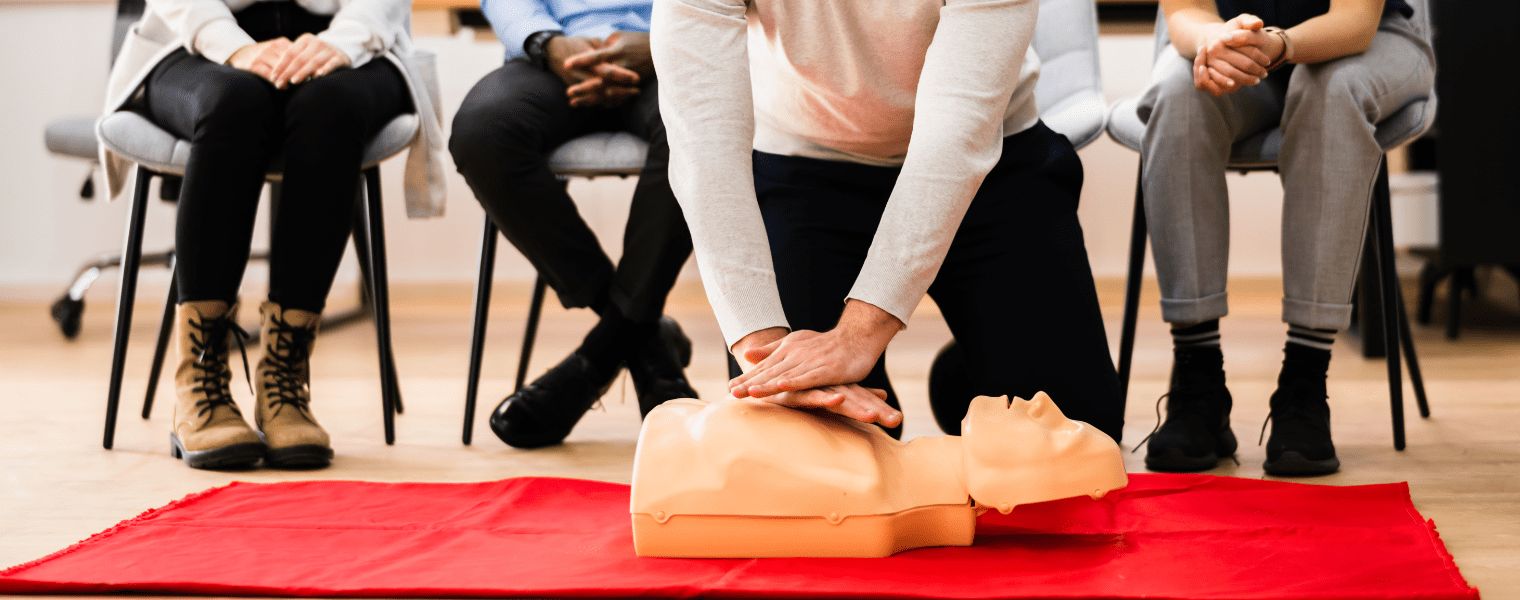
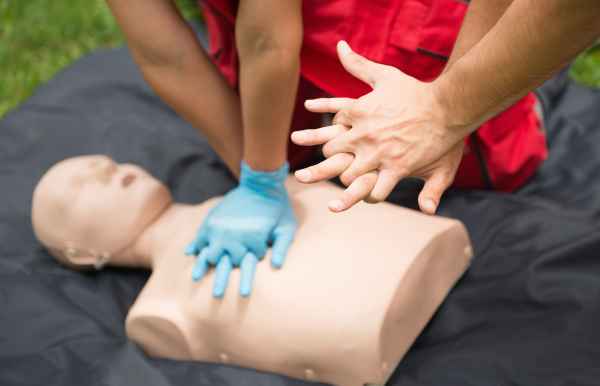
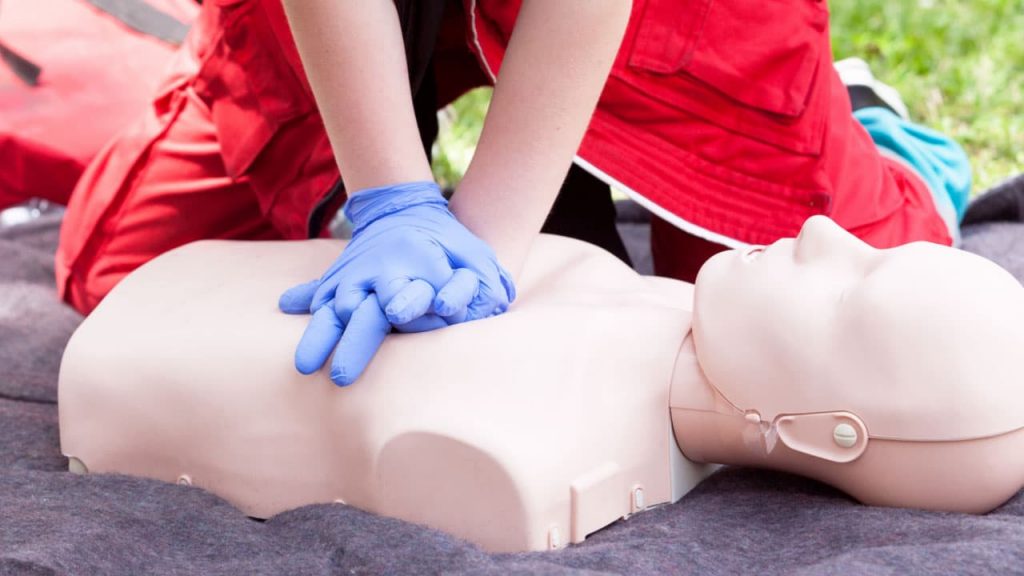
- Perform First Aid: If the victim is unresponsive or not breathing, begin CPR while someone else calls emergency services.To avoid contaminating yourself with the poison, we recommend using a barrier device.
- Move to Fresh Air: If possible, move the victim to an area with fresh air. However, do not enter a hazardous area yourself.
- Avoid Contamination: Prevent further contamination by removing any contaminated clothing. If the chemical has come into contact with the skin, flush the affected area with cool water for at least 15 minutes.
- Monitor and Reassure: Continuously monitor the victim’s condition until emergency responders arrive. Offer reassurance and comfort while awaiting
- Identify the Hazard: If possible, determine the type of chemical involved. This information is vital for emergency responders and medical professionals.
- Avoid Vomiting: Unless directed by medical personnel, do not induce vomiting. This can worsen the situation, especially if the chemical is corrosive.
- Flush Eyes Thoroughly: If the victim’s eyes have been exposed to chemicals, gently rinse them with cool water for at least 15 minutes.
- Cleanse the Skin: If chemicals have come into contact with the skin, remove contaminated clothing carefully and rinse the affected area with cool water for at least 15 minutes.
Buy A First Aid Kit
Take care of any small injuries your family or employees receive with our Multi-Purpose First Aid Kit. Treat them with the wide range of supplies included in this kit.
Workplace Chemical Safety
 Chemical inhalation can be a significant concern in many workplaces. Employers have a responsibility to ensure the safety of their workers by implementing appropriate safety measures. This may include:
Chemical inhalation can be a significant concern in many workplaces. Employers have a responsibility to ensure the safety of their workers by implementing appropriate safety measures. This may include:- Proper ventilation: Maintaining adequate ventilation systems to remove airborne contaminants.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Providing appropriate PPE for workers who may be exposed to chemicals, such as respirators, gloves, and safety glasses.
- Chemical labeling and storage: Ensuring all chemicals are properly labeled and stored safely.
- Training: Providing workers with training on chemical safety procedures, including how to respond to chemical inhalation incidents.
Common Chemicals that are Inhaled
 Understanding the types of chemicals that can cause inhalation incidents is crucial for prevention and response. While countless chemicals pose risks, some common culprits include:Carbon Monoxide (CO): Often referred to as the “silent killer,” carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning fuels like gasoline, natural gas, oil, wood, and charcoal. Exposure to high levels of CO can lead to oxygen deprivation, resulting in serious health consequences or even death.Household Cleaners: Many common household cleaners contain chemicals that can be harmful if inhaled. These include ammonia, bleach, and various bathroom and kitchen cleaners. Always ensure proper ventilation when using these products.Paint and Paint Thinners: The fumes from paints, varnishes, and thinners can irritate the respiratory system. Prolonged exposure or exposure to high concentrations can lead to more severe health effects.Pesticides and Fertilizers: These chemicals are designed to kill pests or promote plant growth, but they can also be harmful to humans if inhaled. Always follow safety precautions and wear appropriate protective gear when handling these products.Industrial Chemicals: Numerous chemicals used in industrial settings can be hazardous if inhaled. These include solvents, acids, and gases used in manufacturing processes. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are essential in these environments.Preventing Carbon Monoxide Poisoning:To reduce the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, follow these guidelines:
Understanding the types of chemicals that can cause inhalation incidents is crucial for prevention and response. While countless chemicals pose risks, some common culprits include:Carbon Monoxide (CO): Often referred to as the “silent killer,” carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning fuels like gasoline, natural gas, oil, wood, and charcoal. Exposure to high levels of CO can lead to oxygen deprivation, resulting in serious health consequences or even death.Household Cleaners: Many common household cleaners contain chemicals that can be harmful if inhaled. These include ammonia, bleach, and various bathroom and kitchen cleaners. Always ensure proper ventilation when using these products.Paint and Paint Thinners: The fumes from paints, varnishes, and thinners can irritate the respiratory system. Prolonged exposure or exposure to high concentrations can lead to more severe health effects.Pesticides and Fertilizers: These chemicals are designed to kill pests or promote plant growth, but they can also be harmful to humans if inhaled. Always follow safety precautions and wear appropriate protective gear when handling these products.Industrial Chemicals: Numerous chemicals used in industrial settings can be hazardous if inhaled. These include solvents, acids, and gases used in manufacturing processes. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are essential in these environments.Preventing Carbon Monoxide Poisoning:To reduce the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, follow these guidelines:- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home and test them regularly.
- Ensure proper ventilation when using fuel-burning appliances.
- Have your heating system and chimneys inspected annually.
- Never use generators, grills, or other fuel-burning equipment indoors.
- Be aware of the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning, which can mimic the flu.
- If you suspect carbon monoxide poisoning, evacuate the area immediately and call emergency services.
Stay Safe and Breathe Easy!
 Chemical inhalation incidents can be a serious health hazard. Being prepared for chemical inhalation incidents can make all the difference. By following these steps and staying informed, you can be a hero in your own life and help others in need. Remember, knowledge is power, and a little preparation can go a long way. Take a First Aid training offered by Coast2Coast to gain hands-on experience and build confidence in handling emergencies. Remember, a few simple steps can make a world of difference in preserving someone’s life.Join our various First Aid classes at Coast2Coast, and become a Canadian Red Cross certified First Aider.
Chemical inhalation incidents can be a serious health hazard. Being prepared for chemical inhalation incidents can make all the difference. By following these steps and staying informed, you can be a hero in your own life and help others in need. Remember, knowledge is power, and a little preparation can go a long way. Take a First Aid training offered by Coast2Coast to gain hands-on experience and build confidence in handling emergencies. Remember, a few simple steps can make a world of difference in preserving someone’s life.Join our various First Aid classes at Coast2Coast, and become a Canadian Red Cross certified First Aider.Register For A First Aid Training
Register today for a First Aid training course and learn how to deal with emergencies and keep your loved ones safe! Check out our facilities and book your spot now.