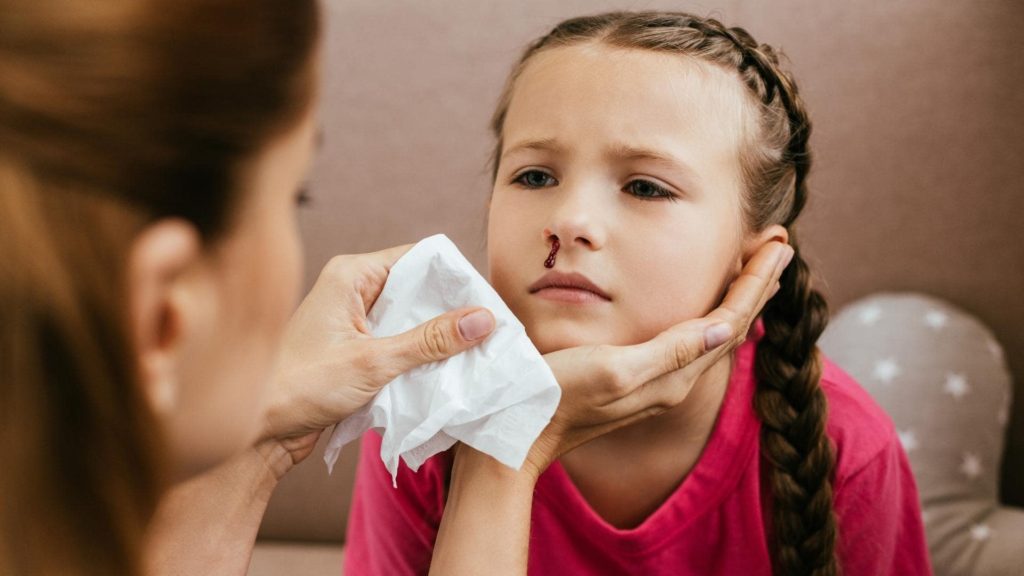
A bleed from the nose is not usually a sign of a severe problem, but it can be pretty frightening. Doctors call nosebleeds epistaxis, which refers to a nosebleed from one or both nostrils. It is usual for a nose to bleed for anything between one and fifteen minutes, and the flow can either be light or heavy. Frequent nosebleeds can indicate a problem and lead to anemia if not controlled.
Why Do Nosebleeds Occur?
Internally, the nose has a profusion of fine and sensitive blood vessels that easily bleed when damaged.
These are common causes of nosebleeds:
- Nose picking
- Blowing the nose too hard
- Minor injuries
- Humidity or temperature changes causing the interior of the nose to become dry and cracked
- Allergies
- Change in air pressure
Nasal bleeding can sometimes occur from the blood vessels situated deeper within the nose—the cause of this type of bleeding can be a knock to the head, the side-effects of nasal surgery, and atherosclerosis (hardened arteries).
People who get nosebleeds more frequently include children between the ages of 2 and 10, the elderly, and pregnant women. Another group of people prone to nosebleeds are those on anticoagulants, people with blood clotting disorders, and those with hypertension.
Learn How To Stop Nose Bleeds
What Not to do With a Nosebleed
There are several things that you must never do with a nosebleed, even if they seem like a good idea.
- Never tip your head back because the blood flows into the back of the throat and may lead to choking.
- Never stuff anything into the nostrils to slow the bleeding because tissues and napkins can irritate the nose lining, causing more bleeding when removed.
- Never lie down because it increases the pressure in the blood vessels.
- Never keep frequently checking on the nosebleed as you apply pressure; otherwise, the bleeding will take longer to stop. Apply the pressure for the recommended time.

How to Stop a Nosebleed
The following are the most effective ways to stop a nosebleed.
- Stay calm or help the other person stay calm, especially a child.
- Stay seated, leaning slightly forward, and firmly pinch your nose on the soft part just above your nostrils. Keep the pressure on for 10-15 minutes until bleeding is controlled. If the nosebleed occurred due to a head injury, do not pinch your nose.
- Avoid blowing, picking and rubbing your nose as this can cause bleeding to begin again.
- For unconscious victims suffering a nosebleed, move them into the recovery position. This will allow the blood to drain without potentially suffocating the victim.
The bleeding should stop with the actions above. However, if it doesn’t, you must seek medical advice. Contact your doctor if:
- You take aspirin or warfarin as an anticoagulant.
- You have a clotting disorder like hemophilia that inhibits the bleeding from stopping.
- You have the symptoms of anemia – heart palpitations, shortness of breath, or a pale complexion.
- A child under two has a nosebleed because this is rare and could indicate another underlying problem.
- You have regular nosebleeds.
How to Prevent Nosebleeds
To avoid nosebleeds :
- Use a humidifier if the air is dry.
- When participating in sports that risk concussions to the nose, wear protective athletic gear.
- Nose blowing should be done gently.
- Children should not be encouraged to pick their noses.
Call emergency services or see a doctor if:
- Bleeding that continues after 15 minutes
- Heavy bleeding
- The person suffered a head injury
After a nosebleed stops, take extra precautions not to start the bleeding again because the blood vessels are sensitive and need to constrict. Avoid blowing or rubbing your nose hard, and don’t put anything inside your nostrils. Also, don’t lift any heavy objects.
First Aid and Nosebleeds
Learn more about nosebleeds in First Aid & CPR training with Coast2Coast. The training offered in a First Aid course teaches you how to deal with nosebleeds, ways to prevent them, and recognize the signs of regular and more severe nosebleeds.
Whether you require a Standard First Aid certificate for your work or want the general knowledge of Emergency First Aid training to help your family and community, Coast2Coast has a training program that suits your requirements.
Register today by choosing the area in Ontario or Toronto nearest to you, and pick the day and time that suits you best.
First Aid training is the best way to prepare to help yourself and others in an emergency.