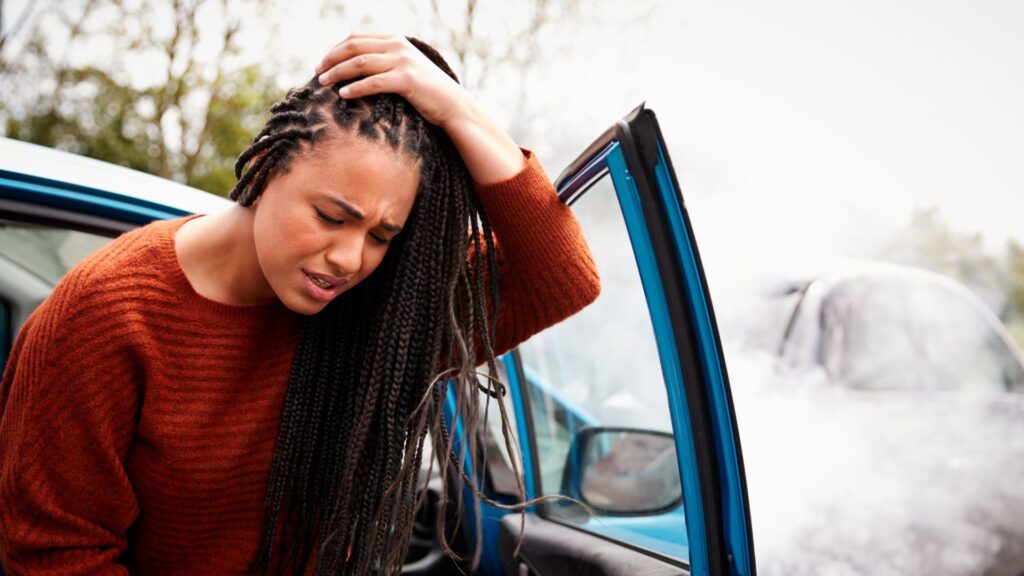
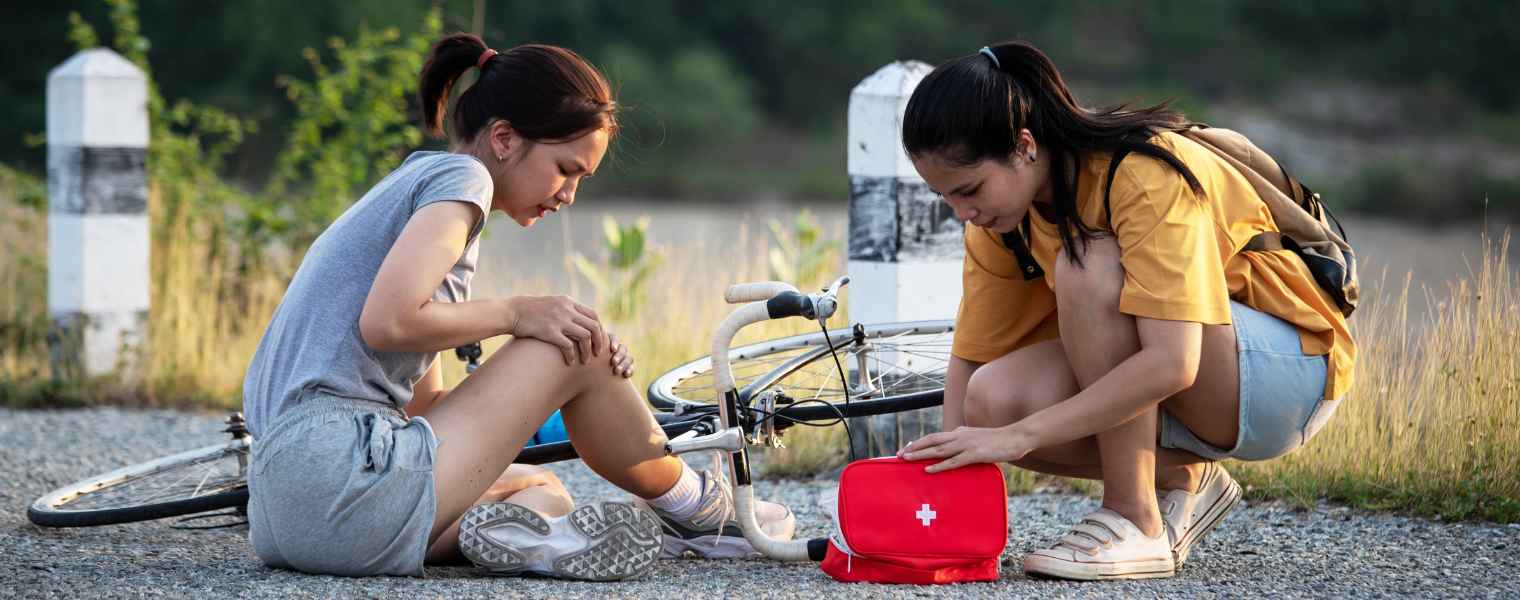
Concussions are extremely prevalent, especially among children who participate in sports. Whether it is getting hit in the head with a basketball, or receiving a punch to the face in karate, concussions occur at home, on the playground, and during extra-curricular activities. Adults, on the other hand, can suffer a concussion from various activities, and the symptoms of concussion in adults can range from headaches to confusion, often resulting from a head injury during physical activity, which in some cases may lead to a serious injury, like brain injury or even cause one to lose consciousness.
Let’s dive into the causes, signs, first aid steps, and prevention tips regarding concussions.
What is a Concussion?
A concussion is a type of brain injury that typically occurs after a person experiences trauma to the head, neck, or body. This form of traumatic brain injury can lead to a variety of concussion symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, and cognitive changes. The impact of a concussion can differ significantly from one individual to another, influencing both physical abilities and mental and emotional health. In some cases, a head injury can also result in brain swelling, further complicating recovery and affecting daily life. Understanding the multifaceted effects of a concussion is crucial for proper treatment and support.
Causes of a Concussion
The causes of a concussion often involve rapid movement of the head, which can cause the brain to shift within the skull, resulting in a brain injury. This quick motion can occur in various ways, including:
A hit to the head
A blunt force to the face or body
Whiplash
Vehicle collisions (motor vehicle accidents)
Sports injuries
Such trauma can lead to symptoms like a severe headache and may result in serious brain injury, as well as damage to the blood vessels in the brain. Recognizing these causes is essential for effective prevention and timely treatment of concussions.

Inquire about First Aid Training
Concussions and other injuries are covered in our Standard First Aid & CPR/AED Level C training course. Contact us today to get registered and learn more!
In the following YouTube short, our instructors explore the crucial signs and symptoms of concussions. Concussions are serious brain injuries that can occur from a blow to the head or body, causing a range of immediate and delayed symptoms. In this video, we’ll discuss common physical symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and confusion, as well as less obvious symptoms such as sensitivity to light and noise, slurred speech and changes in mood or behavior. Understanding these signs is essential for recognizing when medical attention is needed. Let’s dive in!
Concussion Signs and Symptoms
Concussion signs and symptoms can be elusive, as concussions often do not appear on imaging scans like MRIs, X-rays, or CT scans. Therefore, it is essential to monitor for changes in thinking, physical abilities, emotional state, and sleep patterns. Key indicators to watch for include:
Cognitive difficulties, which can signal a disruption in brain function
Physical symptoms such as headaches or dizziness, often linked to a head injury
Emotional changes, which may reflect the psychological impact of traumatic brain injuries
Altered sleep patterns, indicating potential disruptions following a concussion
It’s particularly important to be vigilant if there has been a previous concussion, as repeated concussions can exacerbate symptoms and lead to more severe consequences. If any symptoms of a concussion worsen over time, immediate medical attention is crucial to ensure proper evaluation and care.
Thinking
Concussions can alter your thinking by creating:
- Confusion
- Temporary memory loss
- Slower reaction times
- Issues with concentration
- Difficulty thinking
Physical
The body may also experience out-of-the-ordinary scenarios, such as:
- Dizziness or disorientation
- Migraines
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Clumsiness
- Feeling groggy and not right
- Blurry vision
Emotional
Head trauma may also impact one’s emotional well-being, initiating:
- Sadness
- Nervousness or anxiousness
- Mood, behavioural, or personality changes
- Increased irritability
Sleep
Concussions can also play a role in changes in sleeping patterns:
- Difficulty sleeping
- Sleeping a lot more or less than normal

Other more severe symptoms
- Seizures or convulsions
- Double vision or disorientation
- Loss of consciousness or fainting
- Constant vomiting
- Weak limbs
Symptoms specific to babies and children
Symptoms specific to babies and children can be particularly challenging to recognize, leading to many cases of concussions going untreated. Identifying signs of a concussion in this age group is especially difficult due to their inability to speak or clearly express their feelings. Other symptoms specific to babies and children may include:
Disinterest and inattention towards their favorite foods or toys, which can indicate changes in behavior
Alterations in typical sleeping and eating patterns, signaling potential disruption in their routine
Excessive crying, which may be a sign of distress related to the injury
It is crucial to monitor for these concussion symptoms, as a second concussion can lead to more severe complications if the initial injury occurred without proper treatment. If any symptoms worsen, timely intervention is vital to support concussion recovery and protect brain cells and brain tissue from further damage.
First Aid for Concussions
Symptoms of concussions are often perceived as minor, creating internal and external pressure that may discourage individuals from seeking medical care. For example, if a soccer player experiences a blow to the head, they might choose to continue playing and dismiss any concussion symptoms that arise. However, neglecting a concussion and its proper recovery can lead to further injuries, including serious traumatic brain injury, permanent brain damage, or even death.
That is why addressing a concussion in a timely manner is crucial by:
Immediately stopping any activity following trauma to the head, neck, or body.
Seeking medical help as soon as possible. In Canada, only qualified doctors and nurses can medically assess patients with head injuries through clinical history, physical examination, diagnostics, and specialist referrals.
Continue to monitor your condition and observe for any changes. Recovery from a concussion may take anywhere from 10 days to 4 weeks, with adults typically recovering faster than children.
Additionally, research indicates that men and women may experience different concussion symptoms and recovery patterns, which can influence their diagnosis and treatment plans. Be vigilant for potential issues such as balance problems, trouble walking, or changes in mental function, especially in the case of multiple concussions or mild traumatic brain injuries.
Acute Phase
The acute phase of a concussion is the time period in which the concussion has recently occurred, and the patient is experiencing worsening or the peak of their symptoms. During this phase, it is important for the patient to stop performing activities that require a lot of mental and physical exertion, as the brain and body require plenty of rest. The patient can participate in light activities, such as listening to music, short strolls, and condensed periods of work. However, any activity that further exacerbates symptoms should be avoided.
Recovery Phase
After the acute phase comes the recovery phase. Symptoms should start slowly improving, and the patient can begin gradually returning to regular day-to-day activities. The level of mental and physical exertion a patient can tolerate during this stage is situational and based on symptoms. Typically, medical professionals recommend staying away from exercise and heavy strain on the body until symptoms are gone.
How to Prevent a Concussion
To help prevent concussions take precautionary measures because it is better to be safe than sorry. Be sure to wear your seat belt in the car and never drive or enter a vehicle with a driver under the influence. Don’t forget to wear the proper helmet when biking or playing contact sports while ensuring that it fits correctly. Childproofing your home could also allow your little ones to move and explore without fear of a concussion.
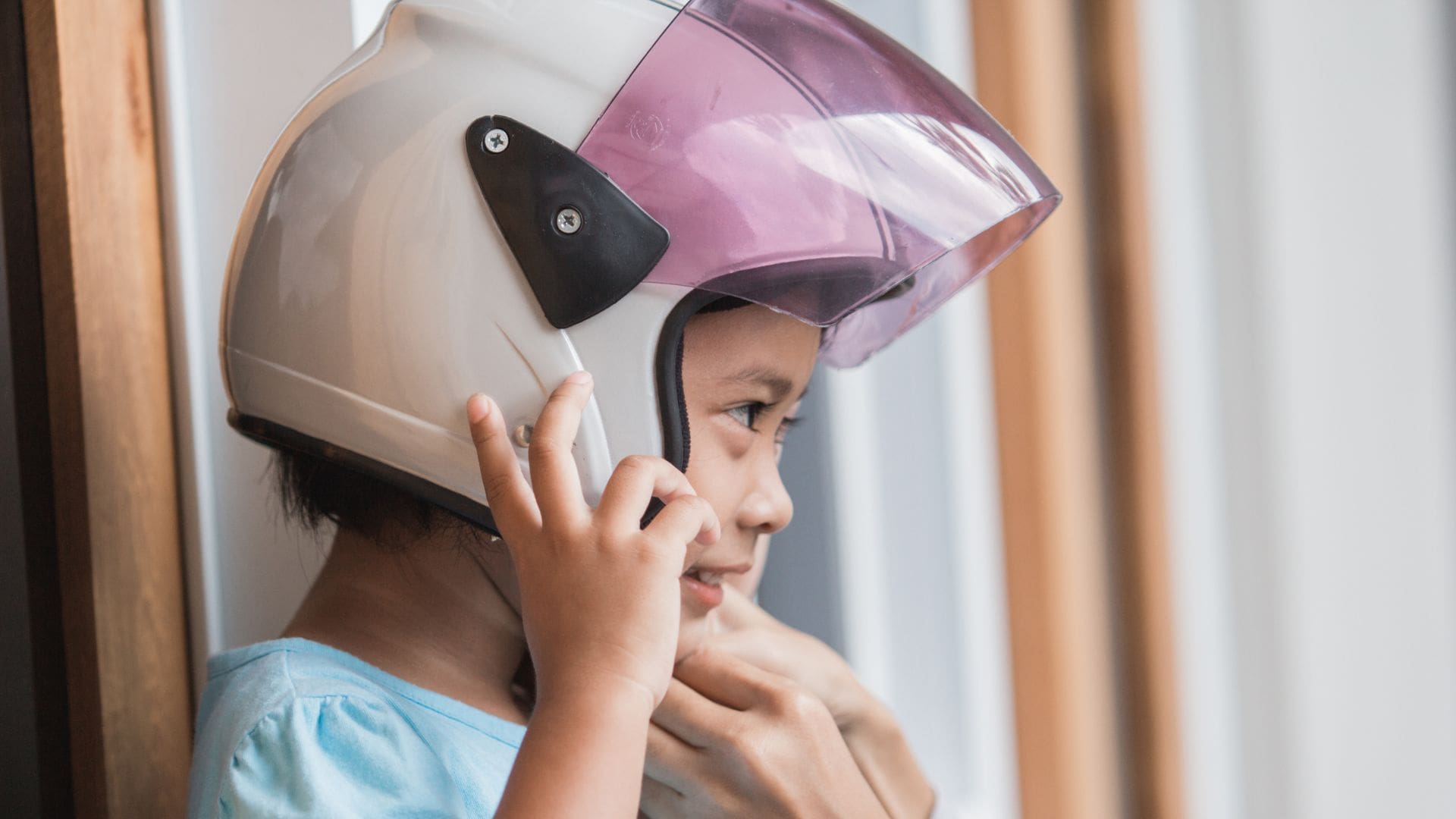

Take a Standard First Aid Training Class
Witnessing your child, friend, or loved one experience a head trauma can make you feel powerless, but standard First Aid training, can equip you with the knowledge and courage to take action in these situations. Register at your closest Coast2Coast location today to begin tackling situations with the proper training and confidence.