Medical emergencies require that you keep calm so you can tackle them efficiently. These are the top 10 first aid emergencies that you will likely face in your lifetime. Basic first aid skills make it easier for you to manage any emergency, whether it’s an injured person who needs immediate care or a serious injury that requires quick intervention. A basic first aid course can teach you how to handle these situations confidently. Always call for emergency medical help, especially when the ambulance arrives is needed to handle the situation professionally. With the right training, you’ll be prepared to assist until help arrives.
1. Burns and scalds
Burns can be caused by fire, friction, or chemicals. Scalds are caused by hot moist substances like steam or oil. Burnt or scalded areas usually turn red, and blisters may form. Depending on the level of the burn, you may notice destruction in deeper tissues, which can lead to further injury.
Immediately place the burnt or scalded area under cool running or standing water for a minimum of 10 minutes. If the area is too large to do this, apply a cold, wet towel to it. Maintain pressure on the area if bleeding occurs. Do not pop blisters; cover them with a clean bandage or gauze. It is also important not to remove fabric from the burn or apply any lotions.
Chemical burns must be treated differently. Brush dry chemicals off the skin prior to rinsing under cool water for at least 15 minutes. While rinsing, be sure to keep uncontaminated areas safe from the chemicals. Contaminated clothes should be removed.
In all cases of burns, it’s crucial to monitor the person’s vital signs, such as their breathing and heart rate, and seek immediate professional help. A basic first aid course can provide you with the skills needed to handle burns and other medical emergencies confidently until help arrives. If the person complains of feeling cold, cover them with a clean sheet or blanket to prevent hyperthermia and get immediate medical attention.
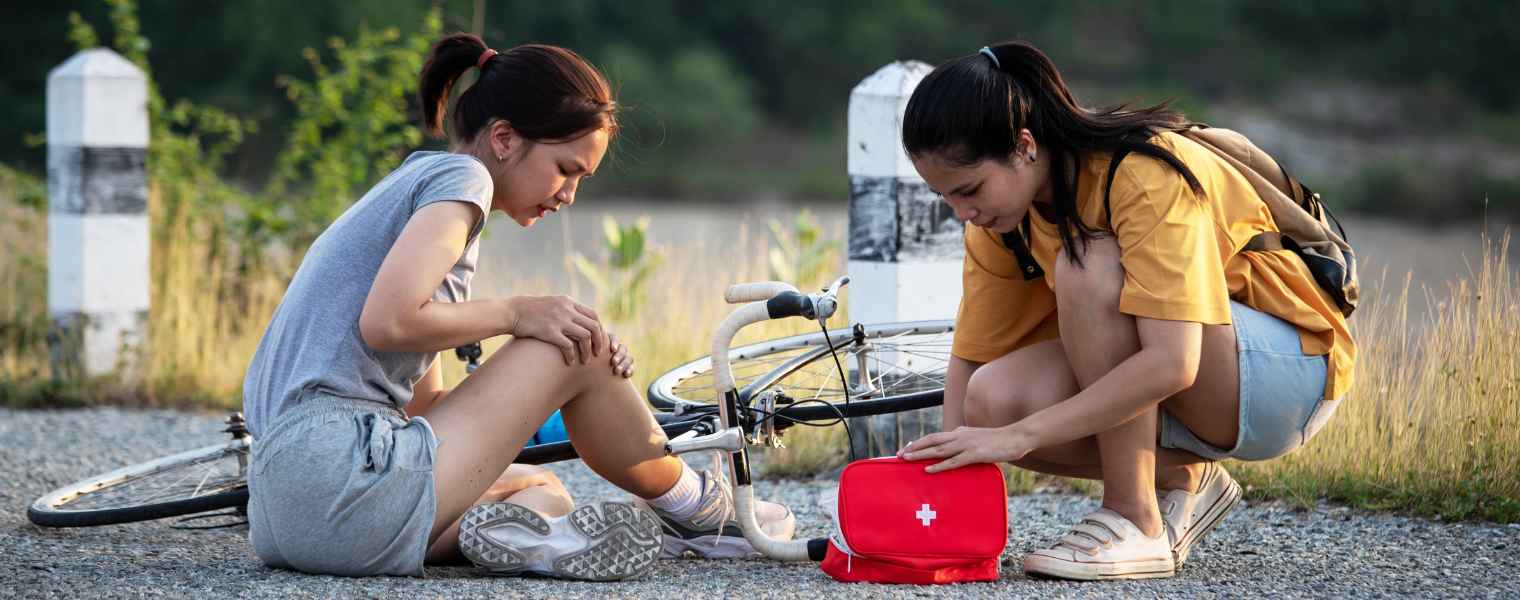
2. Cuts and wounds
You can easily stem a bleed if a cut or wound is small. Rinse with clean water for five minutes, then apply an antibiotic ointment and adhesive bandage. However, for bigger cuts with profuse bleeding, you may need to call for help. Stop the bleeding by tightly holding gauze or cloth over the wound. If you need to apply more gauze, do not remove the first one. Keep applying direct pressure and add another gauze on top. This is part of first aid for managing cuts and wounds effectively.
For more serious medical emergencies, formal first aid training can equip you with the necessary skills to act quickly. Basic first aid techniques, such as controlling bleeding, can be learned in a basic first aid course, helping you manage injuries until professional help arrives. Be sure to have first aid kits readily available in your home or car, as they are essential for treating cuts and other injuries.

Over the next few days, it is important to watch for signs of infection. Seek emergency treatment if:
-
You cannot control the bleeding
-
There is a foreign object in the wound
-
You can see tissue or bone
-
There are signs of infection
Knowing how to treat an injured person and when to seek additional help can make all the difference in a medical emergency.
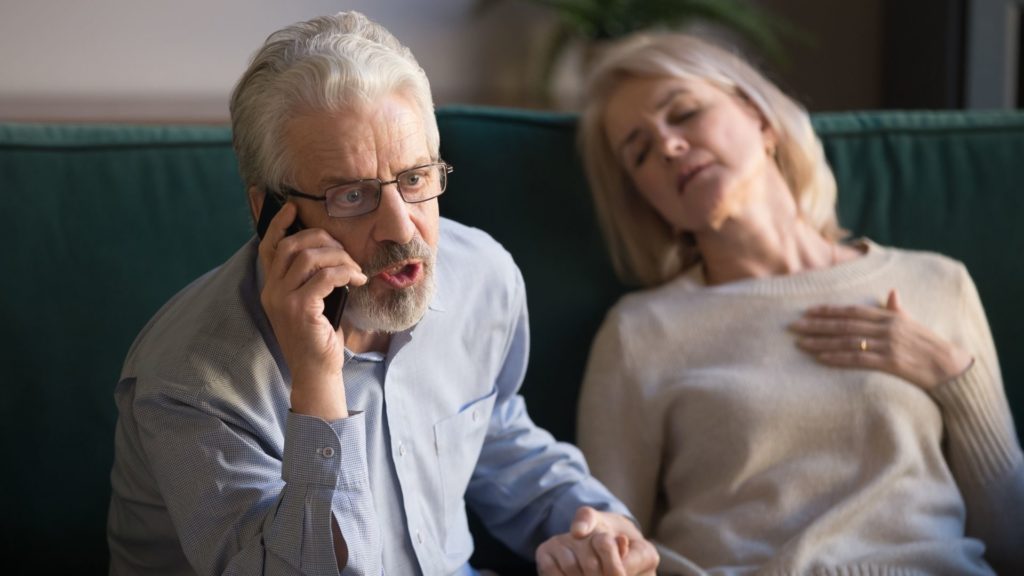
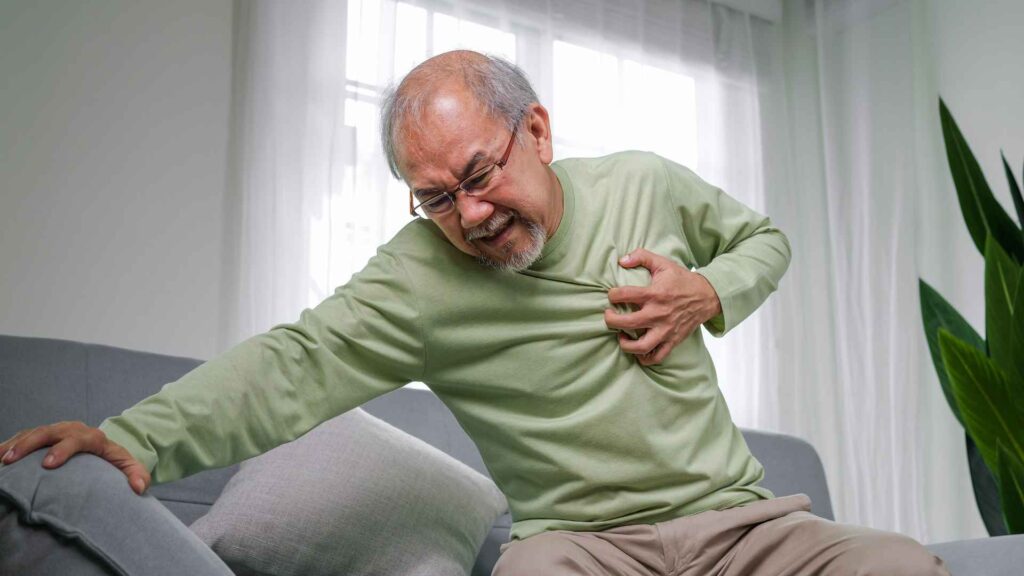
3. Heart attacks
The symptoms of a heart attack differ from person to person and are different in men and women. This is caused by a blocked artery, which stops the supply of oxygen to the heart. Heart attacks are a life-threatening medical emergency. If someone starts with chest pain, immediately call for 911/EMS for help.
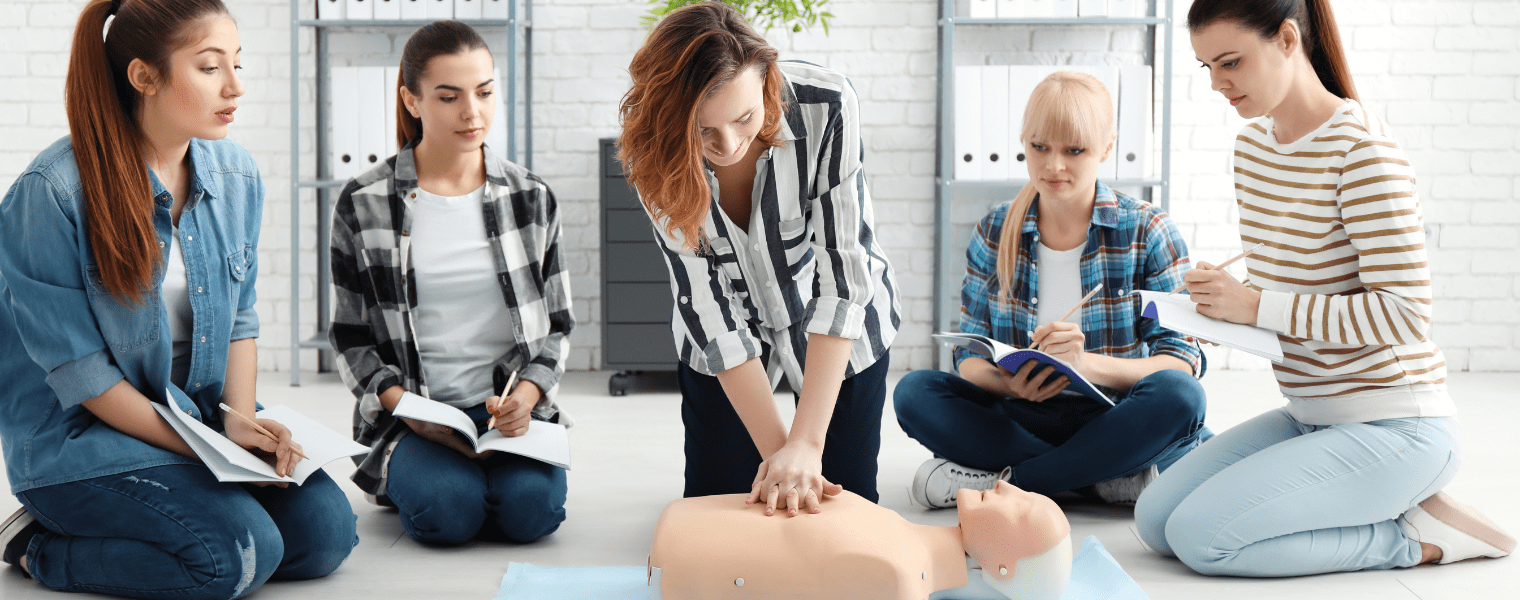
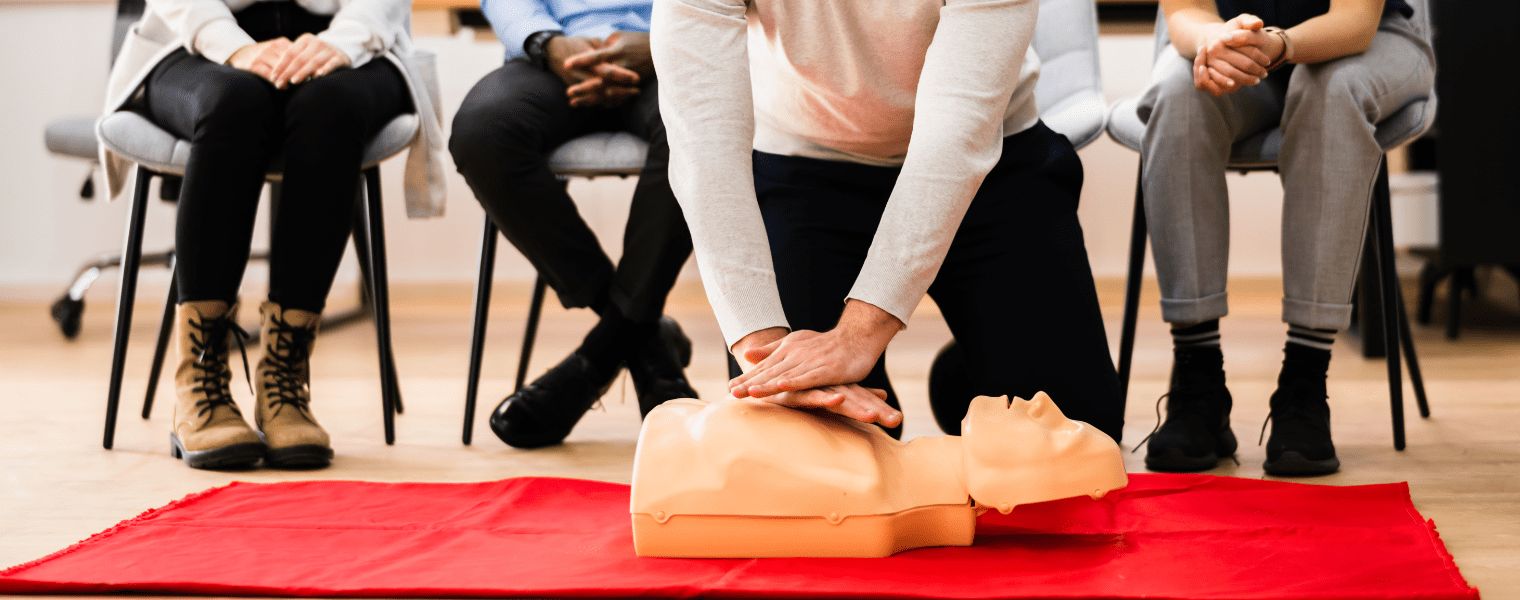
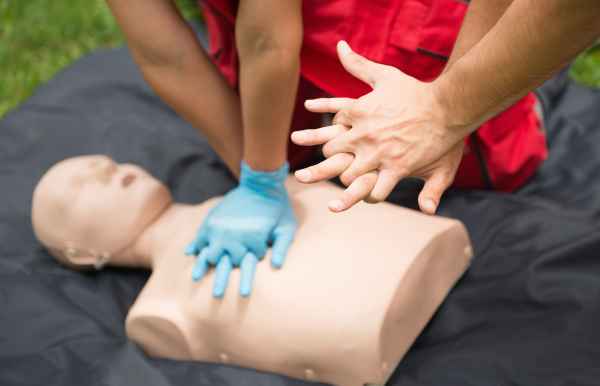
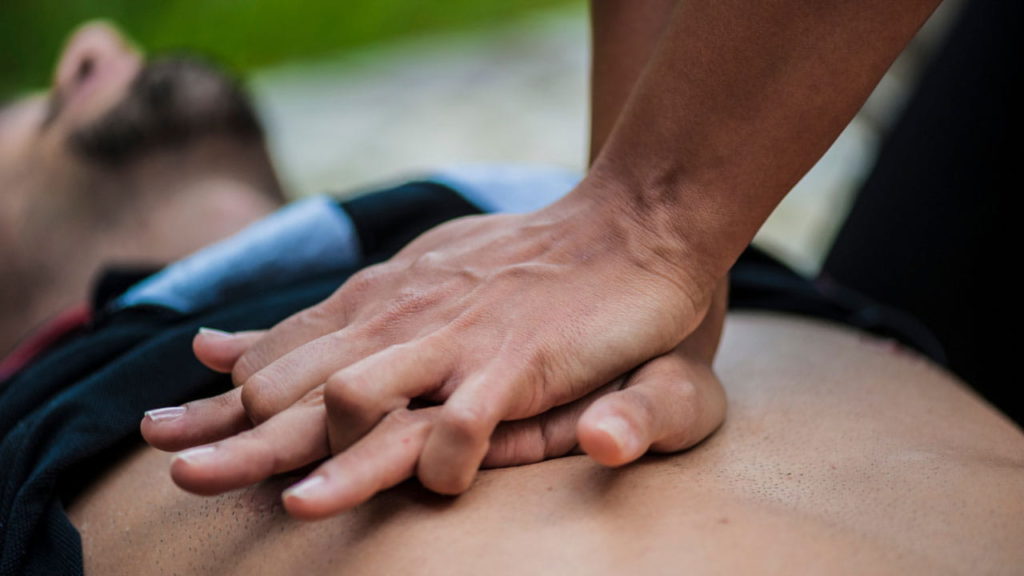
Until EMS arrives, let the person sit in a comfortable position. In case of an unresponsive person, begin CPR with chest compressions on the person’s chest. If you are trained in first aid, continue chest compressions and rescue breathing if necessary. Basic first aid skills, including CPR, can be learned in a basic first aid course and are crucial in handling cardiac arrest situations.
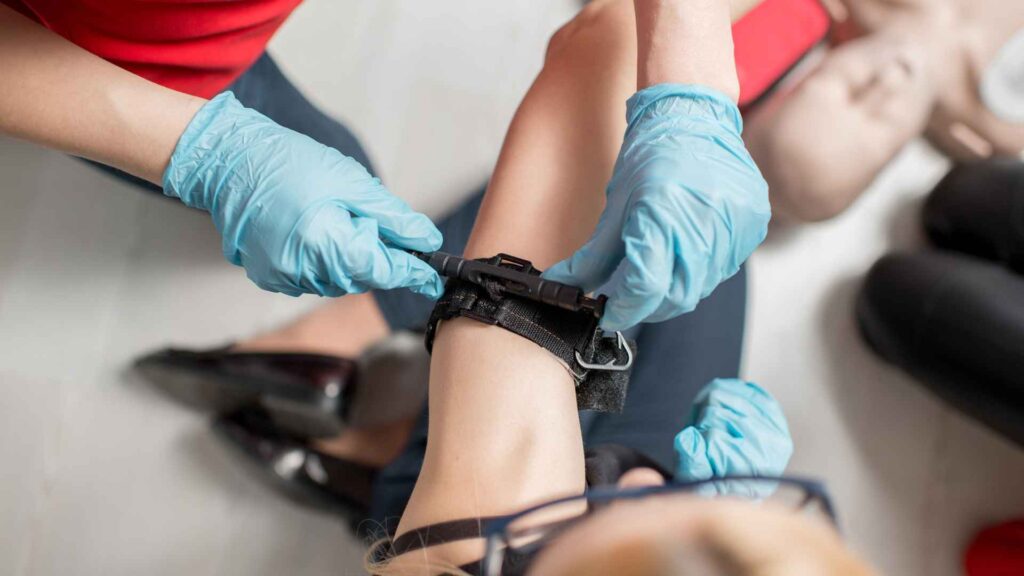
Additionally, having a well-stocked aid kit and first aid kits that include an automated external defibrillator (AED) can be lifesaving. An AED can help restart the heart in the event of cardiac arrest. Knowing how to use an AED properly is a vital part of first aid that can improve the chances of survival in a heart attack or cardiac arrest emergency.

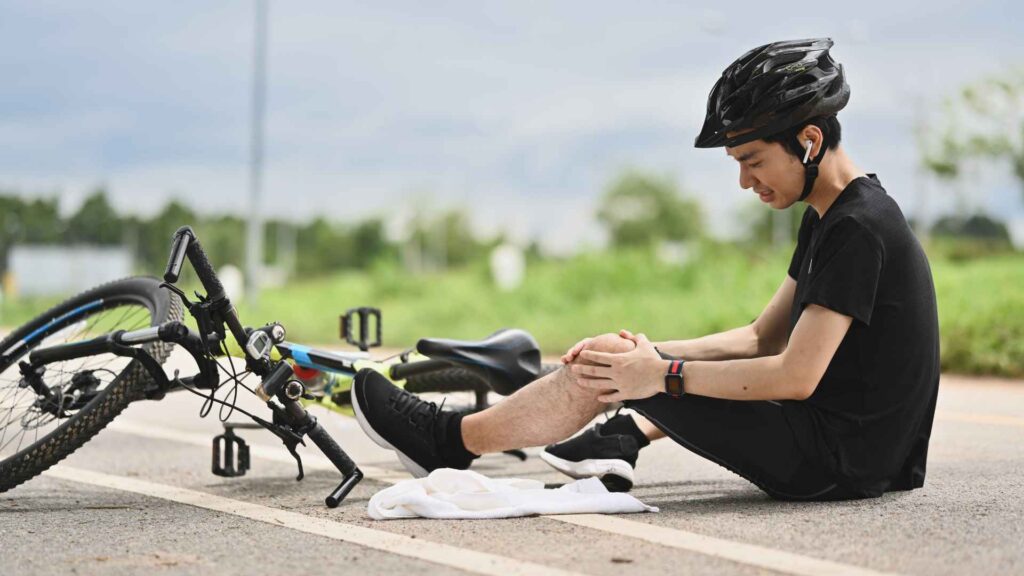
4. Sprains and fractures
Sprains are common injuries and can be treated by elevating the affected area and applying ice to them (RICE method).
Sprains can be difficult to tell apart from a fracture, so a trip to hospital emergencies may be advisable. First aid for sprains can help minimize damage until professional help is available.
- R = REST: do not move or straighten the injured body part.
- I = IMMOBILIZE: splint the injury if you need to move the person or if EMS is delayed. Keep the person still, otherwise.
- C = COOL: keep the injured area cool for 20 minutes every hour, up to 48 hours.
- E = ELEVATE: raise the injured area above the level of the heart if it does not cause the person any pain.
In cases of spinal injury, be extra cautious not to move the person unless absolutely necessary. Basic first aid skills, such as properly stabilizing the injured person, are essential in these situations. A basic first aid course can provide the knowledge you need to manage such injuries confidently.
Fractures or a broken bone need immediate medical attention. Immobilize the limb with the fracture to prevent nerve or blood vessel damage. Also, do not attempt to restore the bone into position. First aid kits should be available to help manage injuries until emergency medical help arrives.
5. Heat strokes and sunburn
Excessive exposure to the sun can cause heat strokes. Heat strokes are a severe illness which is life-threatening. Take the person out of the sun and bring them somewhere cool. From there, you will need to use cooling methods such as immersing them in cool water from the neck down or using ice packs on the chest/armpits. Continue these methods until they improve or EMS arrives. Give the person plenty of liquids to help rehydrate them. It is best to drink something with electrolytes such as Gatorade, coconut water, milk, etc.
Soothe sunburn with cool compresses, aloe vera lotion, and pain relief medication. If the symptoms are severe, including high fever, dizziness, weakness, and oozing blisters, take the person to a doctor.

6. Electrical burns
Electrical burns are important to keep an eye on because they can affect the heart. If the scene is safe, you will need to use caution while working with the person. Look for two burn points (entry and exit points) and care for them as stated earlier in this blog.
In any situation involving medical emergencies, first aid is critical. Basic first aid knowledge, including how to treat burns, can make a significant difference. A basic first aid course will teach you essential skills to help manage such injuries. Always wear disposable gloves to protect yourself and reduce the risk of infection while providing aid care.
Continue to monitor their airway, breathing, and circulation. If the person is in severe pain or shows signs of complications, call 911/EMS immediately. Knowing how to properly assess and respond to electrical burns is an essential part of first aid training.
Be Prepared for Any Emergency!
Join our Emergency First Aid (EFA) course and gain the critical skills needed to respond effectively in urgent situations. Learn from experienced instructors how to provide immediate care and support when it matters most.
7. Bites and stings
Bites from animals can be treated at home if they are small and the animal is not rabid. Wash the wound, apply antibacterial cream and a clean dressing. If the animal is wild or stray, seek medical attention and watch for infection.
Insect stings are also usually harmless unless someone is allergic to bees. In case of an allergy, the person will need to take medication. For severe allergies, call 911/EMS immediately. Otherwise, remove the stinger by scraping it with a plastic card (like a credit card), wash the area with soap and water, and apply an ice pack.

8. Choking
An obstruction in the windpipe causes choking. If the person is unable to cough and cannot breathe, this is called complete choking. You can dislodge the obstruction by using two of three first aid steps: back blows, abdominal thrusts, or chest thrusts. Alternate between the two until the object dislodges.
If the person becomes unresponsive, you will need to begin CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation), checking for the object often. Basic first aid training teaches you how to perform these aid steps effectively, ensuring you can act quickly and correctly. If you are trained in rescue breathing, be prepared to provide it if necessary, as part of your CPR efforts.
For those who are able to cough or speak, have them sit up and cough. This is called partial choking. In all cases of choking, remember to call for emergency help if the obstruction cannot be cleared quickly or if the person’s condition worsens.
9. Seizure
Seizures usually involve jerking and twitching of the body, but the person could also be still and unresponsive. Unless the patient is at risk of hurting themselves, do not try to stop the shaking. Move any objects out of the person’s way and protect their head by putting something soft under it. You will want to roll the person to their side. Make sure they are comfortable and do not put anything into their mouth. Knowing basic first aid for seizures can help you manage the situation until medical help arrives.
If this is the first time a person is having a seizure, they should see a doctor. People who are prone to seizures usually have a medical plan that they follow afterward. A basic first aid course can provide you with the skills needed to handle such medical emergencies confidently. Understanding first aid techniques, including how to assist someone during a seizure, can make a crucial difference in these situations.
10. Stroke
A stroke is caused by a blood clot or bleeding to the brain and is a serious life-threatening condition. If you suspect someone is having a stroke, call for emergency medical attention. You can recognize strokes by applying the acronym FAST which stands for face, arms, speech, and time:
-
F = FACE: changes to the face include a droop to one side of the face, especially noticeable around the mouth and eyes.
-
A = ARMS: a person who has had a stroke will not be able to raise both arms, usually one is weak and numb.
-
S = SPEECH: the person cannot understand you, is slow in responding, and their speech has changed.
-
T = TIME: time is of the essence, if you notice any of these changes, call 911 immediately.

Why First Aid and CPR Training is Important
Accidents and emergencies can happen to anyone at any time. By enrolling in a First Aid and CPR/AED training course, you will learn a variety of life-saving skills which could help in a life or death situation. Coast2Coast First Aid & Aquatics provides First Aid and CPR training which will prepare you for the top 10 first aid emergencies you should be prepared for. Contact us today to register!
Register for First Aid Training
Register today for a First Aid Training course and learn how to deal with emergencies and keep your loved ones safe! Check out our facilities and book your spot now.















No comment yet, add your voice below!